Urgent Care
Diagnosis, treatment, and services for your everyday medical needs such as flu shots and lab work.
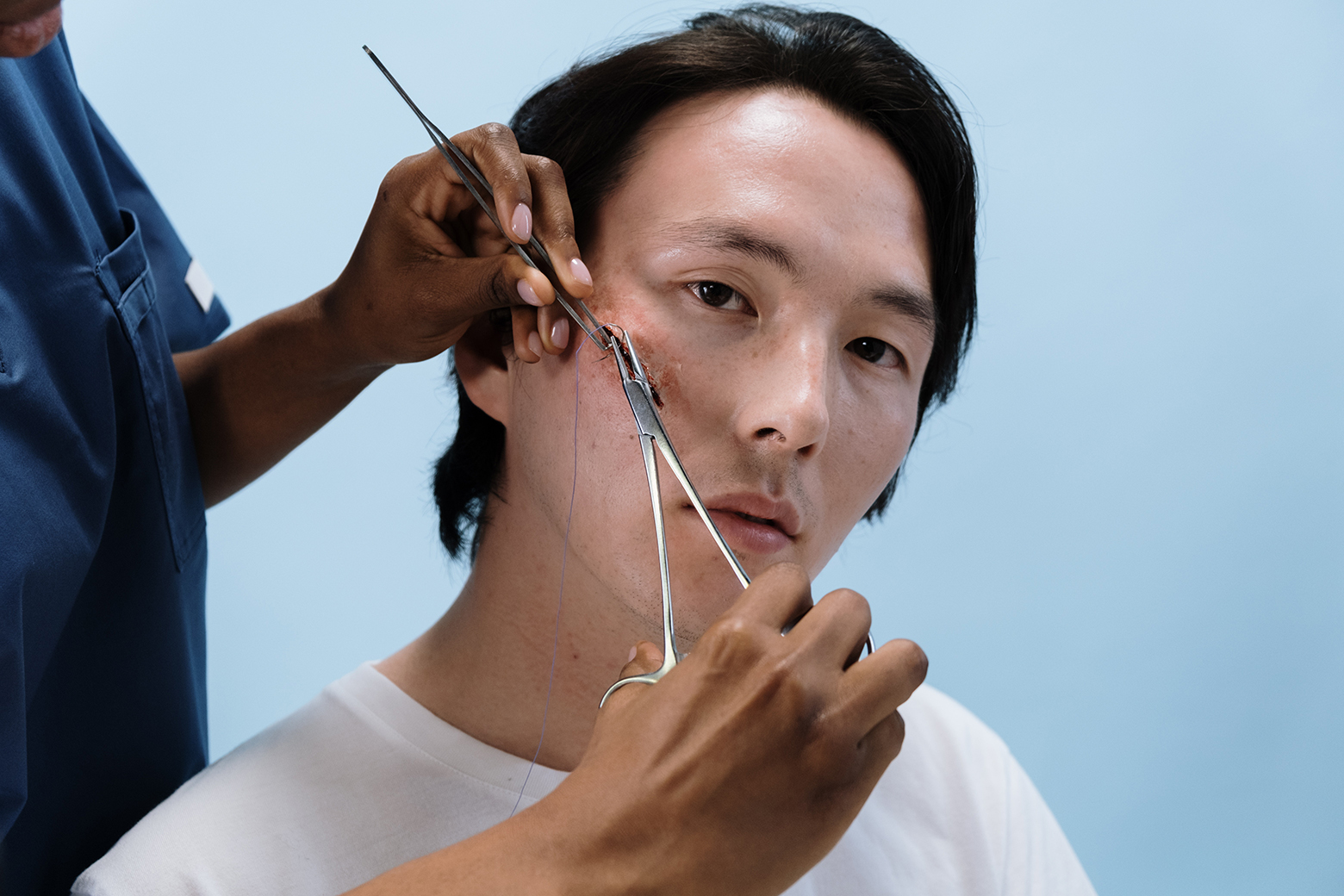

Major or small, we can all think back to a time when we cut, scraped, or grazed ourselves. Sometimes all we needed was a band-aid, other times stitches. Either way, these unexpected accidents happen, especially for kids. Children love to play and sometimes when they’re monkeying around on the jungle gym or the playground, they fall and find themselves with a laceration. As a parent, it can be terrifying to find your son or daughter suffering from an open wound which is why understanding the difference between a deep wound and a shallow one is so important.
A laceration is a tear or opening in the skin caused by an injury. Lacerations may be small and need only minor treatment or may be large enough to require emergency medical care. Wounds such as cuts, scrapes, and lacerations are a split of the skin caused by an impact of some sort. It is common for children to sustain these types of injuries through play, sports, accidents, or ordinary day-to-day activities. Lacerations and other abrasions can happen in almost any area of the body. Depending on the area affected and the severity of the cut, there may be a lot of bleeding or very little.
Minor wounds do not usually require medical attention and can be managed with standard first-aid procedures at home. You should apply pressure to your child’s wound with a clean paper towel or cloth and after removing pressure, the bleeding should slow down or stop altogether. If bleeding continues, reapply pressure and take your child to their healthcare provider for further evaluation.
If bleeding has stopped or slowed, rinse the wound and surrounding area with water. If you can see any dirt or debris in the wound, use a pair of sanitized tweezers to remove any particles. Very small amounts of dirt are OK in grazes but if there are large amounts that you can’t remove, take them to a medical professional who can do it for you.
Lastly, cover the wound with a bandage. This will help to keep the wound clean and will protect the area as it heals. Keeping the wound covered also keeps the wound moist, which helps the healing process.
Like minor wounds, try to stop the bleeding by applying pressure to the injured area. If this doesn’t work and there is a large amount of bleeding that does not quickly stop, or the wound is very deep or is a deep puncture wound, or the wound is gaping apart, despite controlling the bleeding it may need closing with glue or stitches which will require a visit to their healthcare provider.
Stitches are special types of thread that hold wound edges together while they heal. Stitches help to stop bleeding, reduce scarring and decrease the chance of infection in the wound.
Steri-Strips are special adhesive bandages that can sometimes be used on shallow wounds instead of stitches. Steri-Strips perform the same functions as stitches.
Lacerations that involve the face, are longer than 1/2 inch, are deep, or are bleeding heavily, may require stitches.
If your child’s healthcare provider needs to place stitches or use Steri-Strips to close a laceration, you will be given specific instructions on how to care for the stitches. Treatment at home will be based on the place and size of the laceration, the type of stitches used, and any special needs noted by your child’s physician. Sometimes antibiotics are given to help prevent infection in the wound.
Some stitches dissolve and do not need to be removed while other stitches require removal. Your child’s provider will let you know when to return to have stitches removed. It’s important to know that you should not attempt to remove your child’s stitches at home.
For minor wounds, change the bandage whenever it becomes wet or dirty and replace it with a fresh one. Watch for signs of infection as the wound heals and if it seems to not be healing properly, take them to their healthcare provider for evaluation.
Typically, lacerations are no big deal but if your child’s wound doesn’t stop bleeding and the cut looks deep, your best bet is to have them looked at by a medical professional. Wounds can be scary, and no parent wants to witness their son or daughter bleeding, but rest assured, the experts at Chai Care will take great care of your child and will have them as good as new in no time!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.
Feb 21, 2023
Kids are bound to injure themselves at some point or another. Sometimes it’s a broken bone after taking a hard fall, and other times it’s nothing more than a bruise while messing around with their friends. But every now and again a child can cut themselves and believe it to be “no big deal.” Usually, that is the case, unless the wound becomes infected. This is something a parent should keep a close eye on because when a cut or scrape becomes infected, it can lead to much more serious health problems that no parent wants for their child. Knowing the signs of an infected cut and how your child may act when having one is crucial so you can get it treated as quickly as possible before it gets worse.
Most people believe wounds are only caused by accidents, but the truth is anything that breaks the skin is considered to be a laceration because when the skin is broken, there is a risk of germs getting into the body and causing an infection. Skin is the body’s largest organ and helps protect it from bacteria, fungi, and viruses that live on its surface. Depending on the wound’s cleanness, depth, and size, will tell you how much care it needs.
Your healthcare provider will examine the wound and from there decide how they will go about treating it and the wound’s risk of infection. Clean wounds that aren’t contaminated with bacteria have the lowest risk of infection, making them much simpler to care for. Dirty or infected wounds, like an abscess, a deep scrape, or a cut, are a different story. These cuts need special treatment and monitoring to prevent infection. There are times when a wound is clean but there’s a risk of infection because of where it is located. Fluids and other contaminants may get into a wound that’s in an area with more bacteria such as the urinary tract, gastrointestinal system, or respiratory system. Dirt or a foreign object in the wound also can increase the risk of infection.
An infected wound typically gets worse instead of better. Any pain, redness, and swelling will usually increase in intensity making it obvious that the cut needs medical attention. In many ways, this is a good thing that the signs of infection are readily apparent. The first thing you should do with most small cuts and bruises is to apply first-aid. After doing this, monitor the wound for any of the following signs.
If the cut has scabbed over, but the scab keeps on growing, this could be a sign of infection underneath the top-layer skin.
Monitor the cut and speak to your child about what they are feeling. It’s important to make sure that the pain and swelling don’t keep increasing up to 48 hours after the initial injury.
If your child develops a headache or fever, you should take your little one to an urgent care facility for medical treatment. Rest assured, the experts at Chai Care will gladly help!
Most small to medium-sized wounds should heal within ten days. If this is not the case, visit your child’s healthcare provider for further examination.
Increased redness in the region is also a sign of infection. One of the most dangerous signs of infection is the presence of redness that appears to be tracing a path to your child’s heart. This must be treated as soon as possible.
Pay attention to discoloration, such as pus and fluid emerging from the wound.
When the wound is clean, your healthcare provider will close it by stitching the edges together in two separate layers. They will use dissolvable stitches to bring together the deeper layer of tissue under the skin. Then they will staple, tape, or stitch the skin over it. It’s important to note that healthcare experts don’t always close a wound right away. If there’s a chance a wound is contaminated, they will leave it open to clean it out, let’s say in the case that the wound is due to an animal bite. Closing an infected cut can trap bacteria inside which would lead to infection. When they’re sure no bacteria or other impurities remain, they will stitch or close the wound.
Sometimes, it’s best not to sew up a wound at all. If someone has lost a lot of tissues, it’s often beneficial to leave the wound open to heal through natural scar formation. Your child’s provider will also ask about their tetanus vaccine status, to make sure it’s up to date.
Before healing begins, the body gears up to defend itself against any infections. For the first couple of days, a wound may be swollen, red, and painful. This inflammation is a sign of the body’s immune system kicking in to protect the wound from infection. It is important to always keep the wound clean and dry to help the healing process. As the body does its self-healing, a scab begins to form over the wound on the outside. The scab’s job is to protect the wound as the damaged skin heals underneath. Underneath the scab’s defensive surface, new tissue begins to form.
Once the healing is finished, the scab dries up and falls off, leaving behind the repaired skin and a scar. The scar will be roughly 85% of the strength of normal skin and it will take a few months for the scar to be back to 100% strength of normal skin.
Serious wounds won’t heal overnight. It can take weeks for the body to build new tissue which makes at-home care important to prevent infection and minimize scarring. Make sure to keep the wound covered with a clean dressing until there’s no fluid draining from it. Your child’s healthcare provider will give you instructions on how to change the dressing and how often. It’s important to avoid getting the wound wet until further examination. Dirt in the water could seep into the wound and contaminate it. Also, there’s a risk that a wound might pull apart if it gets too wet. Lastly, make sure your son or daughter doesn’t pick or scratch the scab. A scab may itch as the skin underneath heals, but picking or scratching can rip the new skin underneath which will not only increase the healing time but will always make the scar worse.
The best way to help your child is to prevent an infection from ever happening. Any time your son or daughter gets a cut or scrap, the first step is to clean out the injury. Clean the wound with warm water for five minutes, then wash the surrounding area with soap. If there is still debris like glass or dirt in the wound, remove it, but be gentle and avoid pushing down so you don’t push it deeper into the cut. If you can’t remove all the debris or if you don’t feel comfortable trying to remove it yourself, go to an urgent care facility and the staff will do it for you.
Cuts and scrapes are extremely common among children which makes understanding the signs and symptoms of an infected wound so important. Even though infected wounds can have serious consequences, chances are the cut will heal itself on its own or your child’s healthcare provider will supply them with the proper treatment and medication, preventing a dangerous outcome. If the wound does not seem to be healing at home, take your little one to Chai Care and our trained experts will supply them with the care they need!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.

There is no other way of saying it, but we all poop. It’s something every person does and believe it or not, your stool says a lot about your health. With that being said, your child may have a tough time expressing this because of their lack of knowledge and they may be embarrassed to talk about it. It is important for you as the parent to be aware of your child’s bathroom habits so you know if they are ill or if you need to take them to see their healthcare provider. This may not be the most fun information to learn, but it is very important.
Diarrhea is when stools are loose and watery. When experiencing diarrhea, your child may also need to go to the bathroom more often. Diarrhea is a common problem. It may last 1 or 2 days and go away on its own. If diarrhea lasts more than 2 days, your child may have a more serious problem and should be seen by their healthcare provider.
The symptoms your child may experience when they have diarrhea can vary depending on if it’s mild or severe and what the cause of diarrhea might be. Sometimes there is a correlation between serious cases of diarrhea and a medical condition that has gone untreated. It can be tricky because your child may experience all these symptoms or only a few. The main symptom of diarrhea is a loose or watery stool, but other symptoms may include bloating nausea, and an immediate need to use the bathroom. In more serious cases your child may experience fever, weight loss, dehydration, severe pain, and blood in the stool. Severe diarrhea can lead to significant complications and if your child is experiencing these symptoms, call their healthcare provider and seek medical attention.
Believe it or not, there are several different ways to categorize diarrhea.
Acute diarrhea: The most common form. Acute diarrhea is loose watery diarrhea that lasts one to two days. This type doesn’t need treatment and it usually goes away after a few days.
Persistent diarrhea: This type of diarrhea generally persists for several weeks, anywhere from two to four weeks.
Chronic diarrhea: Diarrhea that lasts for more than four weeks or comes and goes regularly over a long period of time is called chronic diarrhea.
Your child’s healthcare provider will ask about their symptoms and health history. They will then give your child a physical exam and if need be, your son or daughter may have lab tests to check their blood and urine. Outside of that, some other tests may include image testing to rule out certain diseases, blood tests, and a stool culture to check for abnormal bacteria or parasites in your child’s digestive tract. This requires a small stool sample to be taken and sent to a lab.
There is also something called a sigmoidoscopy. This test lets the healthcare provider check the inside of your child’s large intestine. This helps to tell what is causing diarrhea, stomach pain, constipation, abnormal growth, and bleeding. The tube is put into your child’s intestine through the rectum, then the tube blows air into the intestine to make it swell.
Identifying the cause of diarrhea can be very difficult, however, the most common cause is typically when a virus infects your bowel. This usually lasts a couple of days and sometimes you’ll hear it being referred to as the intestinal flu. Some other ways your child may have diarrhea would be due to infections by bacteria or pre-formed toxins, eating certain foods, allergies, medications, and in some cases radiation therapy.
Dehydration is the biggest issue when talking about diarrhea. This is more likely the case with young children and those with a weakened immune system. Their dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe. Mild dehydration is the loss of fluid and moderate or severe dehydration puts stress on the heart and lungs. In severe cases, it can lead to shock, which is life-threatening.
Children with viral diarrhea will usually have a fever and may vomit. Soon after these symptoms appear, children will experience diarrhea. It is important to note that part of treating diarrhea is preventing your child from becoming dehydrated.
Treatment will depend on your child’s symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. Dehydration is the major concern with diarrhea and in most cases, treatment includes replacing lost fluids. Antibiotics may be prescribed when bacterial infections are the cause. Children should drink lots of fluids that replenish lost body fluids. If your child is dehydrated, be sure to offer drinks called glucose-electrolyte solutions. These fluids have the right balance of water, sugar, and salts. They should also avoid juice or soda and make sure not to give too much plain water to kids of any age.
When taking over-the-counter drugs, it is important to always follow the instructions. The rules for managing diarrhea in an adult are different than in children, making it important to always call your child’s healthcare provider before giving your child any type of medication for diarrhea.
If your child has severe diarrhea, call their healthcare provider. Young children are at a higher risk of dehydration than adults and you can’t treat a child’s diarrhea the same way you would treat an adult. Over-the-counter medications can be dangerous in young children, and their healthcare provider should manage all diarrhea treatments in children. It’s important to keep your child hydrated. Their provider will decide what is the best way to make sure they stay hydrated, but options often include breast milk, formula, and beverages with electrolytes (for older children, not babies).
In extreme cases of diarrhea, your child may become very dehydrated and because of this, have serious complications. As stated before, dehydration is one of the most harmful side effects of diarrhea and in infants and small children, this can have serious consequences.
If your child has diarrhea that doesn’t seem to improve or resolve completely, you should call their healthcare provider. Pay attention to any other symptoms they may be experiencing which might include fever, vomiting, rash, weakness, numbness, lightheadedness, dizziness, weight loss, and blood in your stool.
At the end of the day, your child’s diarrhea is most likely nothing more than a stomach bug or a bad belly ache. Even though there is a chance it may be something more serious, over-the-counter drugs and plain food complimented with plenty of fluids should do the trick and have your child feeling healthy in no time. But if your little one doesn’t seem to be healing back to their normal selves, our trained staff at Chai Care will be happy to offer our expert advice and top-notch service!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.
Feb 16, 2023
Broken bones are no joke. Injuries like breaks and fractures can have long-term effects if gone untreated and for children, they are that much more serious. Kids are known to horse around, rambunctiously playing without thinking about the consequences which can, unfortunately, lead to sustaining one of these injuries. Thankfully, casting and splinting have given us the ability to heal back to our healthy selves. They help to immobilize the injured limb to keep the bone in place until it fully heals. Of course, everyone has either had or knows someone who has needed a cast or splint, still, they are important to learn about just in case you or your child may need one someday.
Casts and splints are orthopedic devices that are used to protect, and support broken or injured bones and joints. Casts are usually made from fiberglass or plaster and splints are what you would call half-casts and provide less support than casts. Casts differ from splints because they supply more support and safety for a limb that is injured or broken.
Splints provide less support than casts, but the good thing is that they are faster and easier to use. Splints also can be tightened or loosened easily if the swelling in the arm or leg increases or decreases. Ready-made or “off-the-shelf” splints are available in many different sizes and shapes and in more unique cases, custom-made splints are required.
Simply put, casts and splints are used when a bone is broken and can also be used following orthopedic surgery. Sometimes splints are used immediately following an injury due to swelling of the injured area. After the swelling goes down, then a full cast might be applied to the injured limb. Sometimes a cast might have to be swapped during the healing process if the wounded area becomes less swollen and the cast gets looser. If this does happen, the cast might be replaced with a splint to provide more flexibility.
It may not seem important to know, but understanding the types of casts and splints that are available and what they are made of can not only improve your child’s healing process but can also potentially harm your child depending on if they have allergic reactions to specific chemical compounds.
Casts are partly made from fiberglass or plaster, which form the solid layer that protects the injured limb and keeps it restrained. Fiberglass has several advantages compared to plaster. It’s light, making the cast weight loss and comfortable. Fiberglass is the better choice in case the limb must be X-rayed during the healing process, and they are also available in a variety of colors that your child can choose from!
Your child’s cast may or may not be waterproof. The outside of most casts are made of waterproof fiberglass, but the inside liner must also be made of waterproof fabric in order for the cast to be waterproof. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you which cast they have.
Typically, waterproof liners are breathable, and they transfer moisture away from the skin by letting water pass through and drain out which allows air to go into the cast and dry the skin.
Non-waterproof liners are used if your child is allergic to the waterproof liner. These will soak up water and take much longer to dry.
It’s important to investigate problems with blood circulation in the injured limb. A good strategy to use is checking the fingers or toes of the injured limb every day. The fingers or toes should have no swelling or changes in skin color. If you press on a nail bed until it turns white, the color should return to normal within 3 to 4 seconds after you take your finger off the nail. The fingers and toes should not be pale or bluish the temperature of the fingers and toes should feel warm. Also, check the skin around all edges of the cast each day for red, dry, swollen, cracked, blistered, or bleeding areas.
Your healthcare provider will remove the cast with a special cast saw when the bone has healed appropriately. The cast saw has a flat, rounded metal blade that vibrates. But don’t worry! The saw can cut through the cast without injuring the skin underneath. Your child’s physician will then cut the cast in several places, usually along both sides of the cast. After this, the cast will spread and open and a special tool is used to lift it off. Scissors are used to cut through the protective padding and stockinette layers which then are removed.
Complications can range from minor to severe and may vary according to the length of time that the cast is worn. It is best to speak to your child’s healthcare provider if you feel that the cast or splint is causing them harm.
Pressure sores are one injury that may occur. These are sores that develop on the skin under the cast. This can happen because the cast was too tight or did not fit correctly, causing excess pressure on one area.
There is also something called Compartment Syndrome. This is a complication caused by a tight or rigid cast that constricts a swollen limb. When the pressure inside the cast builds, it can cause damage to the muscles, nerves, or blood vessels in the space covered by the cast. The damage may be permanent if it is not discovered and treated promptly. Call your child’s healthcare provider or visit the emergency room immediately if you notice that your child has numbness or tingling in the affected limb, cold or pale skin, burning or stinging, or increased pain or swelling.
Even though we live in a world where your child can receive a cast or splint and make a full recovery, it is still important to promote safe play and educate them on how to protect themselves. Kids love to mess around and sometimes that leads to an injury, but this is no reason for them not to still be their energetic selves. The good news is that if your child does wind up needing a cast or splint, the experts at Chai Care will always be here to supply your little one with a perfectly mounted cast or splint!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.
Jan 30, 2023
It’s fair to say we all have had a nosebleed at some point in our lives. They are extremely common and can happen for many reasons, but when you see a child with one, they are that much more frightening, especially if you’re the parent of the child. A million questions race through your mind, concerned and panicked that it is due to a broken nose or a head injury. Fortunately, we live in a world with plenty of methods to treat a nosebleed, one of them being nasal cauterization—a simple procedure that can drastically improve your child’s quality of life.
Nasal cautery, or nasal cauterization, is a procedure used to treat nosebleeds, also known as epistaxis. This procedure is when a chemical or electrical device is applied to the mucous membranes in the nose to stop the bleeding. This is performed with topical anesthetics, usually in an operating room under general anesthesia. Sometimes this procedure is performed in conjunction with other procedures to improve nasal breathing such as sinus surgery, nasal endoscopy, or septoplasty.
Typically, children benefit from nasal cautery when they have recurrent nosebleeds. These episodes can occur from a prominent blood vessel in the nose that bleeds from trauma (nose picking, rubbing the nose, or bumping the nose), and from drying of the mucous membranes lining the nose. Certain underlying medical conditions can make children more prone to nosebleeds, including individual or familial bleeding disorders, platelet disorders, cancers, or medications used to treat other conditions.
If an underlying medical condition or medication is the cause of the nosebleeds, first attempts are aimed to treat or to remove these sources of the tendency for bleeding. In addition, nasal creams, ointments, gels, nasal saline spray, and increased environmental humidification can help improve nosebleeds by decreasing the dryness in the nose. This makes the nose less prone to bleeding and for young children, it’s best to avoid nose-picking. If nosebleeds continue despite these attempts, nasal cautery may be recommended.
The procedure is typically performed either in the pediatric ENT clinic procedure room or in an operating room. The procedure only takes 5-10 minutes but may take longer depending on the severity and any additional combined procedures planned. The surgeon will provide an idea of how much time is expected, but this may change during the procedure.
After the procedure, your child may be asked to stay in the hospital, but in most cases, this won’t happen. When home, Tylenol or Ibuprofen is typically appropriate for pain control. Sometimes stronger narcotic pain medications may be prescribed for additional pain control. Also, the use of topical moisturizing and/or antibiotic ointment in the nose is recommended after the procedure. This will help with healing and decreases crusting. If the child develops any concerning symptoms after the procedure, including pauses in breathing, color change of the skin (particularly if the lips, face, or hands are turning blue), appearing lethargic or tired, severe bleeding, or any other sudden change from his/ her normal behavior, please seek immediate medical attention.
As we know, nose cautery can help prevent nosebleeds. The healthcare provider uses a chemical swab or an electric current to cauterize the inside of the nose. This seals the blood vessels and builds scar tissue to help prevent more bleeding. For this procedure, the provider will numb the inside of your child’s nose and once the procedure is finished, your child may feel itching and pain in the nose for 3 to 5 days but not to worry, over-the-counter pain medicines can help with the pain! Keep in mind, your child may want to touch, scratch, or pick at the inside of the nose. Make sure to watch your child carefully so you can stop them before any touching or picking because this will cause more nosebleeds.
It’s important to keep a lookout for any signs of distress in your child and to know when you should contact your provider. If your child has pain that does not get better after your child takes pain medicine, they get another nosebleed and the nose is still bleeding after you have pinched the nose shut 3 times for 10 minutes each time, they have a fever or if your child does not get better as expected, then it may be time to bring your child back in for a check-up.
Afterthought
If you feel that your child may need nasal cauterization, it’s best not to wait, hoping they will get better on their own. We live in a country that has more than enough reliable healthcare providers, Chai Care being one of them! Our trained experts will always be here to help in a time of need and will make sure your youngster is back to normal in no time!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.

As bad as breaking a bone or burning yourself can be, most consider infections to be worse due to their ability to spread and potentially come back again. Children are some of the most vulnerable people to contracting a virus because they typically have worse hygiene habits and are less knowledgeable of the signs and symptoms. Cellulitis is definitely one of those bacterial infections to watch out for because if left untreated it can lead to more serious issues.
Cellulitis is a deep bacterial infection of the skin that usually occurs after some type of trauma causes an opening in your child’s skin. Typically, the infection involves your child’s face, arms, and legs. In most cases, human or animal bites or injuries that occur in water can also cause infection and immediate treatment can help prevent the spread of cellulitis. In some cases, cellulitis is considered an emergency and your child’s healthcare provider may treat your child in the hospital depending on the severity of their condition.
Cellulitis is a tricky infection because many of the symptoms may appear as something less significant. If your child has swollen or warm skin, bruising, chills, a fever, or a red streak from the original site of pain, there is a good chance they have cellulitis. In some cases, cellulitis is considered an emergency and you should consult your child’s healthcare provider if the area affected is causing your child to complain of numbness, tingling, or other changes in a hand, arm, leg, or foot, if the skin appears black, or if the area that is red and swollen is around your child’s eyes or behind the ears.
The diagnosis of cellulitis is usually based on the medical history and physical examination of your child. Blood and skin samples may also be taken to confirm the diagnosis and the type of bacteria present.
Specific treatment for cellulitis will be determined by your child’s healthcare provider based on your child’s age, overall health, and medical history. However, treatment may include oral or intravenous antibiotics, warm, wet dressings on the infection site, surgical intervention, and rest.
If your child’s arm or leg is affected, their provider may also have you elevate the extremity and decrease the amount of activity. Also, based on the physical examination, your child’s physician may treat your child in the hospital depending on the severity of the cellulitis. In the hospital, your child may receive antibiotics and fluids through an intravenous catheter.
Complications can be reduced with prompt and accurate treatment by your child’s provider. The most common complications include meningitis, septic arthritis, and an infection of a joint caused by glomerulonephritis.
To prevent cellulitis, protect the skin from cuts, bruises, and scrapes. This isn’t easy, especially for active kids or those who play sports. It’s best if your child uses elbow and knee pads, wears a bike helmet when riding, shin guards, long pants, long-sleeved shirts while hiking in the woods, and sandals on the beach.
If your child does get a cut or scrape, wash it well with soap and water followed by applying an antibiotic ointment, then cover the wound with an adhesive bandage or gauze and lastly, check the wounds often for the first few days to see if any signs of cellulitis begin.
You should contact your provider if any area of your child’s skin becomes red, warm, and painful — with or without fever and chills. This is even more important if the area is on the hands, feet, or face, or if your child has an illness or condition that suppresses the immune system. Also, if your child gets a large cut or a deep puncture wound but most importantly if an animal bites your child, especially if the puncture wound is deep, contact your provider immediately. Cellulitis can happen quickly after an animal bite. Even human bites can cause skin infections too, so call the doctor if this happens.
To recap, cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin that often happens in areas where the skin is broken. Because of this, it’s important that your child always washes their hands before and after touching the infected area to make sure it doesn’t get any worse. With that being said, there are only so many at-home options at your disposal which is why Chai Care will always be here to offer top-notch aid!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.

It is every parent’s worst nightmare to see their child with an injury, especially when it is something as serious as a fracture or dislocation. These are extremely common childhood injuries because young children have bones that are growing and are not yet fully developed, making them more fragile than adult bones. Because of this, it is paramount to understand the best ways how to keep your youngster safe, as we all know how adventurous and energetic kids can be. However, there are some important differences between a fracture and a dislocation that are crucial to know so as not to confuse the two.
Simply put, a fracture is a term used for a broken bone. They can occur in any bone of the body, but the most common fractures in children are in the wrists, arms, and elbows, which usually occur after a fall in most cases, the injury will heal well and cause no long-term complications.
Older children will usually be able to tell you where they are in pain and can explain what exactly happened to better understand the situation. This can make it easier to identify if the injury is in fact a fracture or potentially something more significant. It can be more difficult to identify a fracture in infants or toddlers due to their lack of communication skills. They may cry and not use the affected area, rather than articulate what they are feeling.
A dislocation is a joint injury. It occurs when the ends of 2 connected bones come apart. Fortunately, it is not common in younger children! This is because their growth plates are weaker than the muscles or tendons. Growth plates are the areas at the end of long bones where the bones grow, making them more common in teens and adults.
A dislocation happens when extreme force is put on a joint. It can occur if your child falls or takes a hit to the body, such as while playing a contact sport. It’s important to note that when a dislocation occurs, ligaments can be torn—these being flexible bands of fibrous tissue, joining various bones and cartilage. They also bind the bones in a joint together. The hip and shoulder joints, for example, are called ball and socket joints. Lots of force on the ligaments in these joints can cause the head of the bone (ball) to come out of the socket partly or fully. The most dislocated joint is the shoulder.
Now that we know what both a fracture and a dislocation are, it’s time to discuss how we go about treating them.
In most cases, if your child has a fracture, they will need to restrict movement of the injury site to allow the bone time to heal. Some fractures may require a splint or a partial cast, held in place with bandages. A splint or partial cast helps to support the injured area, allowing the bone to rest and heal while also providing your child pain relief. A splint or partial cast generally does not have to be worn for as long as a full cast. Casts are required for three weeks to three months depending on the type and location of the injury – your healthcare provider will estimate how long it will be required.
If the injury has caused the bones to move out of place, your healthcare provider will need to move the bones back into the correct position which is known as a “reduction.” These procedures are usually done under sedation or anesthesia in the emergency department or operating room. Fractures that require a reduction will need a full plaster cast (one that wraps around the limb) to allow the injury to heal. Full plaster casts stay on your child for up to three months, depending on the injury.
Treatment for a dislocation will depend on your child’s symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the injury is; however, all dislocations need medical care right away to prevent additional injury because untreated dislocations can lead to serious problems. One of the most common forms of treatment is R.I.C.E. which stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation of the dislocated area. Other forms of treatment would be casting, splinting, repositioning, and in serious cases, surgery.
Whether it be a fracture or a dislocation if your child was wearing a cast and once it has been removed, your child’s skin may be dry and itchy. Bathe the skin with warm soapy water, and apply a plain, non-perfumed moisturizer.
After a fracture, children normally regain strength by engaging in gentle activity and play. Physiotherapy is usually not needed. Your healthcare provider will give your child specific advice about when and how they can return to sport, in most cases four to six weeks later. If your child had surgery, full-contact sports should be avoided for two to three months, but you should discuss this with your child’s healthcare provider.
It is highly probable that at some point your child is going to face one or possibly both injuries. Rather than looking at it as a negative thing, it’s better to see it as a sign that your child is a typical kid who is active and enjoys playing with their friends. When that day does arrive, you can be your child’s hero by understanding the signs, symptoms, and methods on how to take care of them, but even with your newfound knowledge, the experts at Chai Care will always be here to help!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.
We are blessed to live in a world that has dozens of options for us to heal and rejuvenate ourselves—vaccines being the most important. Thanks to all the doctors and scientists of the world, we now don’t have to be frightened of getting sick, however, when talking about children, vaccinations are that much more important because of their ability to prevent certain illnesses before they ever happen. There are cases where babies are born with protection against some diseases because their mothers pass antibodies (proteins made by the body to fight disease) to them before birth, but getting your child vaccinated is still crucial to their overall health.
Immunization (vaccination) is a way to create immunity to some diseases. Sometimes this is done by using small amounts of a killed or weakened germ that causes the disease. Other times the vaccine is simply a small piece of the germ, such as a protein or a piece of its genetic material.
Germs can be viruses (such as the measles virus) or bacteria (such as pneumococcus). Vaccines stimulate the immune system to react as if there were a real infection. It fends off the “infection” and remembers the germ. Then, it can fight the germ if it enters the body later.
For good reason, childhood vaccines can seem overwhelming when you are a new parent. Vaccine schedules recommended by agencies and organizations, such as the CDC, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the American Academy of Family Physicians cover just about 14 different diseases. These vaccinations not only protect your child from deadly diseases, such as polio, tetanus, and diphtheria, but they also keep children safe by significantly decreasing harmful diseases that used to spread from child to child.
It’s important to know that vaccines are dead, weakened versions, or part of the germ that causes the disease in question. When children are exposed to a disease in vaccine form, their immune system, which is the body’s germ-fighting machine, can build antibodies that protect them from contracting the disease when they are exposed to the actual disease. However, over the years, vaccines have generated some controversy over safety, but no convincing evidence of harm has been found. And although children can react to any vaccine, the important thing to know is that the benefits of vaccinations far outweigh the possible side effects.
In most cases, a child gets vaccinated between birth and 6 years. Typically, vaccines are given more than once, at different ages, and in combinations. This means that you should keep a careful record of your child’s shots. Although your healthcare provider will also keep track, people change physicians, records get lost, and the person ultimately responsible for keeping track of your child’s immunizations is you!
Ask your child’s healthcare provider for an immunization record form. This form is incredibly important and every parent should keep it with their other essential documents. Also, you can download an easy-to-read immunization schedule and record form at the CDC website.
Even though most parents and providers do a great job of keeping up with immunizations, studies show that about one-fourth of preschool children are missing at least one routine vaccination, which is important to know because most states will not let your child begin school without a complete immunization record. Sometimes a vaccination is missed when a child is sick, but no matter what the reason, it’s important to make up missed immunizations.
If your child has missed a vaccination shot, you don’t have to go back and start over as the previous immunizations are still good. Your doctor will just resume the immunization schedule, and if for any reason, your child receives additional doses of a vaccine, you shouldn’t sweat it as your child will still need any future doses according to the recommended schedule.
Although vaccines are combined to reduce the number of shots needed, the list is still long. So, to give an easy breakdown here is a typical immunization schedule recommended by age 2.
One vaccination for measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR).
Four vaccinations for influenza, a common upper respiratory infection that can also cause meningitis.
Three to four polio vaccinations (IPV).
Four vaccinations for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DPT).
Three vaccinations for hepatitis B.
One vaccination for varicella (chickenpox) no earlier than age 12 months and only if your child does not develop chickenpox on his or her own (must be verified by a health care provider).
Three vaccinations for rotavirus, a type of infection that causes severe diarrhea.
Four vaccinations for pneumococcal disease, a common cause of ear infections and pneumonia.
From age 4 to 6, your child will need booster shots for DPT, IPV, MMR, and chickenpox. Children should also start receiving a yearly flu shot after the age of 6 months. A vaccination for hepatitis A is recommended for all children. This is a lot to keep track of and why you need an immunization records form.
There are some parents who may hesitate to have their kids vaccinated. The concern is that their child might have a serious reaction or get the illness the vaccine prevents, but the components of vaccines are weakened or killed and in some cases, only parts of the germ are used. Thus, making them unlikely to cause any serious illness. Some vaccines indeed cause mild reactions, such as soreness where the shot was given or a fever however, serious reactions are rare. The truth is that the risks of vaccinations are small compared with the health risks of the diseases they’re intended to prevent.
At the end of the day, immunizations are one of the best ways to protect your family from contagious diseases. Vaccinations have allowed us to live more freely and be less frightened of all the illnesses our unforgiving world has to offer, and luckily, the friendly staff at Chai Care will always be here to give your child the medicine they need to live a beautiful life.
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.

Among the most common injuries a young child can face, ear infections are smack in the middle. They cause extreme discomfort for anyone who has had the misfortune of enduring them and even an adult will tell you how truly irritating they are. Sadly, kids get them regularly for several reasons, but as a person gets older, ear infections tend to happen less frequently. Besides knowing the signs and symptoms of this nasty infection, it’s important to know exactly how they start and why they occur, so you can greatly reduce the odds of your child ever having one!
Chances are you will hear the commonly used term “ear infection”. In the medical world, it is referred to as acute otitis media or a sudden infection in the middle ear (the space behind the eardrum). The truth is anyone can get an ear infection, however, they are one of the most common reasons young children visit healthcare providers.
In many cases, ear infections clear up on their own. Your healthcare provider may recommend a medication to relieve pain and if it has worsened or not improved, your healthcare provider may prescribe an antibiotic. In children younger than the age of two years, an antibiotic is usually needed for ear infections.
It’s important to see your healthcare provider to make sure the ear infection has healed or if your child has ongoing pain or discomfort. Hearing problems and other serious effects can occur with ongoing ear infections, frequent infections, and when fluid builds up behind the eardrum.
Essentially, ear infections are caused by bacteria and viruses. Many times, they begin after a cold or other respiratory infection. The bacteria or virus will travel into the middle ear through the eustachian tube, and the bacteria will plant its nasty self and take control. This tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. The bacteria or virus can also cause the eustachian tube to swell, thus making the tube so swollen that it will become blocked. This will cause the normally produced fluids to build up in the middle ear instead of being able to be drained away.
Another issue is that the eustachian tube is shorter and has less of a slope in children than in adults. This physical difference makes these tubes easier to become clogged and more difficult to drain. The trapped fluid can become infected by a virus or bacteria, causing pain, which is why children are more susceptible to ear infections.
We have been using the term “middle ear” quite a bit and if you’re wondering why it is because it’s rather important to know. The middle ear is behind the eardrum and is also home to the delicate bones that aid in hearing. These bones are the hammer, anvil, and stirrup. This is also where the infection will take hold and live during its duration of time. In addition to the middle, there are also the outer and inner parts of the ear. The outer ear is the outside external ear flap and the ear canal, and the inner ear contains the snail-shaped labyrinth that converts sound vibrations received from the middle ear to electrical signals. The auditory nerve carries these signals to the brain.
Even though the infection will reside in the middle part of the ear, understanding the body part in its entirety can help your child when they tell you where they feel the pain and exactly what they’re going through. Some children will become so vexed by the irritation that they will struggle with articulating exactly how they feel so it’s best to be aware as much as you can.
There are plenty of symptoms to look out for and your child will tell you all about them. The most obvious is ear pain. This symptom is obvious in older children and adults, but in infants and children too young to speak, look for signs of pain like rubbing or tugging ears, crying more than usual, trouble sleeping, and acting fussy/irritable. Other signs to watch out for would be loss of appetite, irritability, poor sleep, fever, drainage from the ear, and trouble hearing.
Ear infections are the most common childhood illness other than a cold. They occur most often in children who are between ages 3 months and 3 years and are common until age 8. Some 25% of all children will have repeated ear infections. Adults can get ear infections too, but they don’t happen nearly as often as they do in children.
It is also important to note that people with certain allergies, chronic illnesses, and even your ethnicity can affect how often your child gets an ear infection. It’s important to know your family’s medical history so you can provide your child’s healthcare provider with the proper information that can prevent any potential threats.
Your healthcare provider will look at your or your child’s ear using an instrument called an otoscope. A healthy eardrum will be pinkish-gray in color and translucent. If an infection is present, the eardrum may be inflamed, swollen, or red.
Your physician may also check the fluid in the middle ear using a pneumatic otoscope, which blows a small amount of air at the eardrum. This should cause the eardrum to move back and forth. The eardrum will not move as easily if there is fluid inside the ear.
Another test they may perform is called tympanometry. This uses air pressure to check for fluid in the middle ear. This test doesn’t test hearing. If needed, your healthcare provider will order a hearing test, performed by an audiologist, to determine possible hearing loss if you or your child has had long-lasting or frequent ear infections or fluid in the middle ears that are not draining.
Your healthcare provider will also check your throat and nasal passage and listen to your breathing with a stethoscope for signs of upper respiratory infections.
Treatment of ear infections depends on age, the severity of the infection, the nature of the infection, and if fluid remains in the middle ear for a long period. Your healthcare provider will recommend certain medications to relieve your child’s pain and fever. If the ear infection is mild, depending on the age of the child, your healthcare provider may choose to wait a few days to see if the infection goes away on its own before prescribing an antibiotic.
Antibiotics may be prescribed if bacteria are thought to be the cause of your child’s ear infection. Then, your provider may want to wait up to three days before prescribing antibiotics to see if a mild infection clears up on its own when the child is older. If your or your child’s ear infection is severe, antibiotics might be started right away.
Even though the chances of your child experiencing an ear infection are extremely high, this shouldn’t be of much concern if you act quickly and are knowledgeable of your family’s health history. Chances are the infection won’t last very long and as your youngster ages, it will soon become a bad memory. Even though there are many over-the-counter drugs and at-home remedies you can use to help heal your child, the healthcare experts at Chai Care will happily take a look as they supply their expert knowledge and quality care!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.

Out of every injury a child can get, head trauma is considered to be the scariest. They can lead to all sorts of issues, especially later in life, which is why it is paramount to be as informed as humanly possible. The truth is head injuries can happen from many things, not just direct blows to the head or contact sports which is why understanding the signs and symptoms of them are even more crucial to be aware of.
Unfortunately, head trauma is common in children and teens. They can hurt the scalp, skull, brain, or blood vessels. They can be as mild as a bump on the head, or more serious, like a concussion. In kids, most are mild and don’t injure the brain. A head injury is a broad term that describes an extensive array of injuries that occur to the scalp, skull, brain, and underlying tissue and blood vessels in the child’s head. Head injuries are also commonly referred to as brain injury, or traumatic brain injury, depending on the extent of the head trauma.
In most cases, head injuries in childhood are due to falls and slips, however, they can also occur from car crashes, bike accidents, sports injuries, and child abuse. These are the most common methods, but the truth is there are many other ways your child may sustain head trauma.
Essentially there are two different types of head injuries: external and involving the scalp and internal involving the skull, brain, or blood vessels.
It’s also important to know that injuries can potentially cause a concussion, contusion, fracture, or bleeding. If this does happen, you should bring your child to their healthcare provider immediately for further observation.
The list can be very long for the signs of a head injury depending on the severity of your child’s injury but the most important symptoms to look out for would be a swollen scalp, headache, loss of conciseness (in serious cases), confusion, irritability, ringing in the ear and fatigue. Again, head injuries can be complicated and even discrete which is why if you fear your child may be experiencing one, you should take them to their healthcare provider for a professional opinion.
Healthcare providers diagnose head injuries by asking questions about how the injury happened and doing a careful examination of the head and checking to see how the nerves are working. Most children with a mild brain injury don’t need medical tests, however, providers will often do a CAT scan of the head if the injury is more serious. In this case, your child may need to get blood tested, X-rayed, or receive an MRI.
You should contact your health care provider immediately if your child had a head injury is an infant, has lost consciousness, even for a moment, wines of head and neck pain (younger children who aren’t talking yet may be fussier), vomits more than one time, won’t awaken easily, becomes hard to comfort, or isn’t walking or talking normally.
If your child is not an infant, has not lost consciousness, and is attentive and behaving regularly after the fall or blow, put an ice pack or instant cold pack on the injured area for 20 minutes every 3–4 hours. If you use ice, always wrap it in a washcloth or sock. Ice placed right on bare skin can injure it. Watch your child carefully for the next 24 hours. If the injury happens close to bedtime or naptime and your child falls asleep soon afterward, check in a few times while they sleep. If your child’s skin color and breathing are normal, and you don’t sense a problem, let your child sleep unless the doctor tells you otherwise. There’s no need to keep a child awake after a head injury. It’s also important to trust your gut. If you think your child doesn’t seem to be acting like they normally do, partly awaken your child by sitting them up. They should fuss a bit and attempt to resettle. If your child still seems very drowsy, try to awaken them fully. If you can’t wake your child, call your healthcare provider or 911 for an ambulance.
The hard truth is that you can’t protect your child from every injury, but you can help prevent head trauma with precautions and by teaching them how to play safely. Your child should always wear a bike helmet that fits well and use the proper sports equipment for inline skating, skateboarding, snowboarding, skiing, and contact sports. Make sure they wear a safety seat or seatbelt every time they’re in the car and if they do sustain a head injury, wait until their healthcare provider says it’s OK before returning to rough play or sports. If the brain gets injured again while it’s still healing, it will take even longer to completely heal.
Head Trauma is a scary injury that no parent wishes to see their child suffer from. This is why by understanding the signs and symptoms of them and teaching your child how to safely play, you greatly reduce the risk of your child sustaining any sort of head injury. It’s an unfortunate part of life that we all get banged up every now and again but the team of dedicated staff members at Chai Care will always make sure to be here if your child ever needs a helping hand!
* Legal disclaimer: The content of this article and the entire Chai Care blog is for educational purposes only; it does NOT constitute medical advice and must not be considered as such. Please consult a medical professional regarding any symptoms or health concerns you or your loved ones.